MOSFETs are widely used. Now some large-scale integrated circuits are used MOSFET, the basic function and BJT transistor, are switching and amplification. Basically BJT triode can be used where it can be used, and in some places the performance is better than the triode.
Amplification of MOSFET
MOSFET and BJT triode, although both semiconductor amplifier device, but more advantages than the triode, such as high input resistance, the signal source almost no current, which is conducive to the stability of the input signal. It is an ideal device as an input stage amplifier, and also has the advantages of low noise and good temperature stability. It is often used as a preamplifier for audio amplification circuits. However, because it is a voltage-controlled current device, the drain current is controlled by the voltage between the gate source, the amplification coefficient of low-frequency transconductance is generally not large, so the amplification ability is poor.
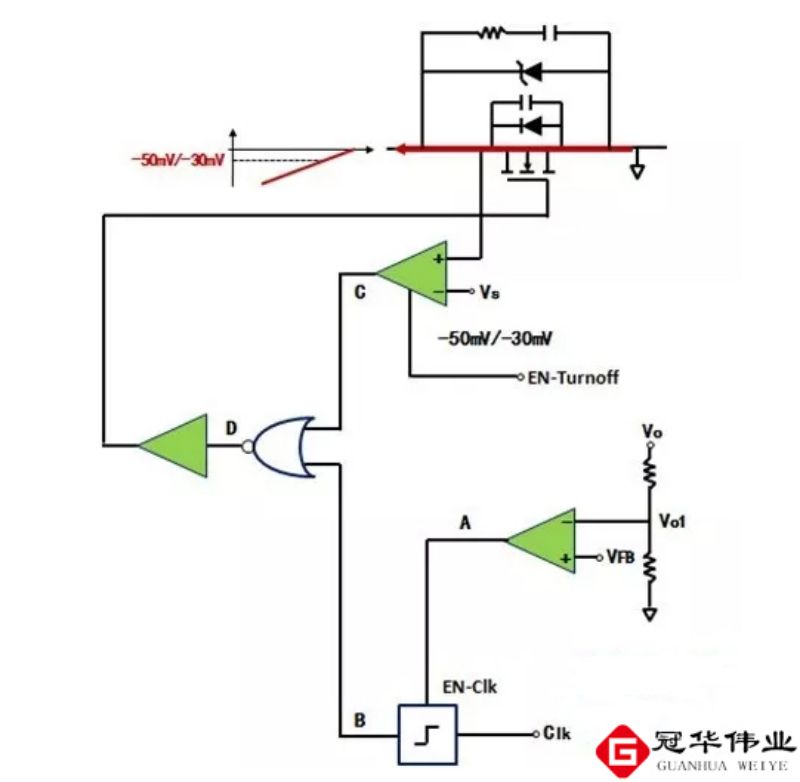
Switching effect of MOSFET
MOSFET used as an electronic switch, due to only rely on polyon conductivity, there is no such as BJT triode due to the base current and the charge storage effect, so the switching speed of the MOSFET is faster than the triode, as a switching tube is often used for high-frequency high-current occasions, such as switching power supplies used in the MOSFET in the high-frequency high-current state of the work. Compared with BJT triode switches, MOSFET switches can operate at smaller voltages and currents, and are easier to integrate on silicon wafers, so they are widely used in large-scale integrated circuits.
What are the precautions when using MOSFETs?
MOSFETs are more delicate than triodes and can be easily damaged by improper use, so special care should be taken when using them.
(1) It is necessary to select the appropriate type of MOSFET for different usage occasions.
(2) MOSFETs, especially insulated-gate MOSFETs, have a high input impedance, and should be shorted to each electrode when not in use to avoid damage to the tube due to gate inductance charge.
(3) The gate source voltage of junction MOSFETs cannot be reversed, but can be saved in the open circuit state.
(4) In order to maintain the high input impedance of the MOSFET, the tube should be protected from moisture and kept dry in the use environment.
(5) Charged objects (such as soldering iron, test instruments, etc.) in contact with the MOSFET need to be grounded to avoid damage to the tube. Especially when welding insulated gate MOSFET, according to the source - gate sequential order of welding, it is best to weld after power off. The power of the soldering iron to 15 ~ 30W is appropriate, a welding time should not exceed 10 seconds.
(6) insulated gate MOSFET can not be tested with a multimeter, can only be tested with a tester, and only after access to the tester to remove the short-circuit wiring of the electrodes. When removed, it is necessary to short circuit the electrodes before removal to avoid gate overhang.
(7) When using MOSFETs with substrate leads, the substrate leads should be properly connected.