Fundamental Principles of MOSFET Switching
Key advantages of using MOSFETs as switches:
- Extremely low on-resistance
- Fast switching speeds
- High current handling capability
- Minimal power dissipation
- No static power consumption in gates
MOSFET Operating Regions in Switching Applications
| Operating Region | Characteristics | Application Use |
|---|---|---|
| Cut-off (Off State) | VGS < VTH | Switch fully off, minimal leakage |
| Linear/Triode (On State) | VGS > VTH, VDS < (VGS – VTH) | Switch fully on, minimal resistance |
| Saturation | VGS > VTH, VDS > (VGS – VTH) | Avoid for switching applications |
Circuit Configuration and Design Considerations
Essential Design Parameters
- Gate drive voltage requirements
- Load current specifications
- Switching frequency considerations
- Power dissipation management
- Protection circuit implementation
Gate Drive Requirements
| Drive Parameter | Typical Range | Design Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Gate Voltage (VGS) | 5V – 12V | Must exceed VGS(th) by adequate margin |
| Gate Current | 100mA – 2A peak | Determines switching speed |
| Gate Resistance | 10Ω – 100Ω | Controls switching characteristics |
Switching Speed Optimization
Factors Affecting Switching Speed:
- Gate resistance value
- Gate drive voltage level
- Input and output capacitances
- PCB layout considerations
- Temperature effects
Protection Circuits and Safe Operating Area
| Protection Type | Implementation Method | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Overcurrent Protection | Current sensing resistor + comparator | Prevents device failure due to overcurrent |
| Overvoltage Protection | TVS diode or voltage clamp | Guards against voltage spikes |
| Thermal Protection | Temperature sensor + shutdown circuit | Prevents thermal runaway |
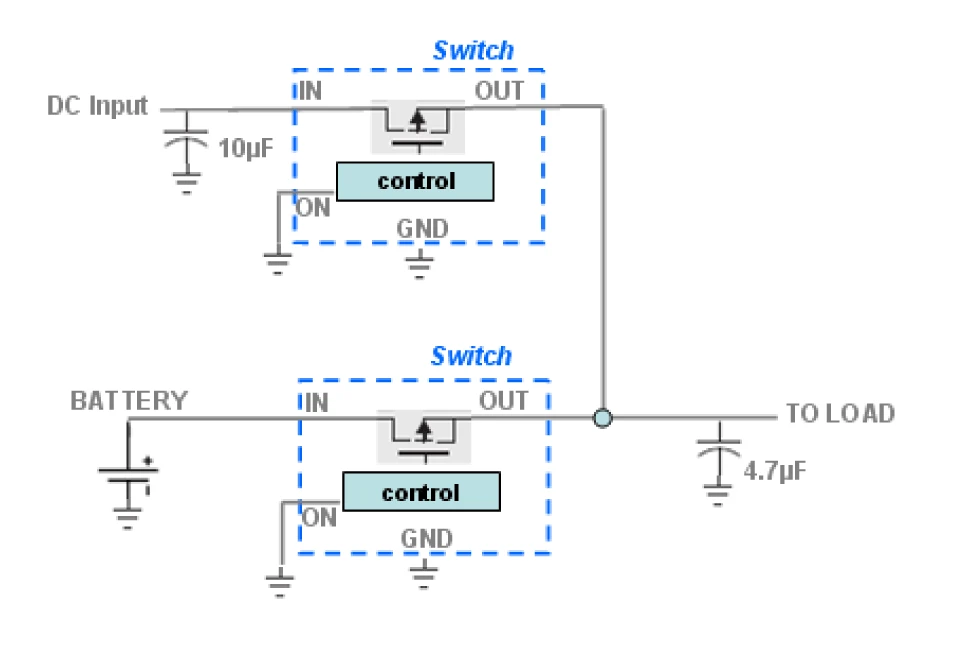
Application Circuit Examples
Low-Side Switching Configuration
Advantages of low-side switching:
- Simpler gate drive requirements
- Direct logic-level compatibility
- Easy current sensing implementation
- Cost-effective solution
High-Side Switching Configuration
Benefits of high-side switching:
- Load referenced to ground
- Better short-circuit protection
- Improved system safety
- Compatible with floating loads
Comprehensive Comparison: Low-Side vs High-Side MOSFET Switching
Understanding the distinctions between low-side and high-side MOSFET switching is crucial for optimal circuit design. Let’s explore their characteristics, advantages, and challenges in detail.
Basic Configuration Differences
| Aspect | Low-Side Switch | High-Side Switch |
|---|---|---|
| MOSFET Position | Between load and ground | Between power supply and load |
| Source Terminal | Connected to ground | Connected to power supply |
| Load Connection | Connected to power supply | Connected to ground |
Low-Side Switching Detailed Analysis
Advantages:
- Simple gate drive requirements – gate can be driven directly from microcontroller
- Lower cost implementation
- Easier to implement current sensing
- No level shifters or charge pumps needed
- Better switching characteristics due to stable source reference
Disadvantages:
- Load is not referenced to ground
- Potential ground lifting issues
- Safety concerns in some applications
- EMI considerations due to switching ground node
- Not suitable for applications requiring grounded loads
High-Side Switching Detailed Analysis
Advantages:
- Load remains referenced to ground
- Better short circuit protection
- Improved safety in many applications
- No ground disruption
- Preferred for automotive and industrial applications
Disadvantages:
- More complex gate drive requirements
- May require level shifters or charge pumps
- Higher implementation cost
- More complicated current sensing
- Bootstrap capacitor may be needed for N-channel implementations
Application-Specific Selection Guide
| Application Type | Recommended Configuration | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Control | High-Side | Better protection, reduced EMI |
| LED Driving | Low-Side | Simple implementation, cost-effective |
| Battery Protection | High-Side | Enhanced safety, better short circuit protection |
| Digital Logic | Low-Side | Easy integration with MCUs |
| Automotive Systems | High-Side | Industry standard, safety requirements |
Design Considerations Matrix
| Design Factor | Low-Side Impact | High-Side Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Gate Drive Complexity | Simple, direct drive possible | Complex, may need special drivers |
| Current Sensing | Straightforward implementation | Requires high-side current sense techniques |
| Protection Features | Basic protection sufficient | Advanced protection features needed |
| Cost Implications | Lower overall cost | Higher due to additional components |
| PCB Layout | Simpler layout requirements | More critical layout considerations |
Expert Tips from Winsok:
- For high-side switching with N-channel MOSFETs, consider our WS-DRIVER series gate drivers for optimal performance
- In low-side applications, use our WS-LS series with integrated protection features
- For automotive applications, our AEC-Q100 qualified WS-AUTO series provides reliable high-side switching solutions
- Consider parasitic effects in both configurations and implement appropriate snubber circuits when necessary
PCB Layout Guidelines
Critical Layout Considerations:
- Minimize gate loop inductance
- Separate power and signal grounds
- Optimize thermal management
- Place gate drive components close to MOSFET
- Consider EMI/EMC requirements
Why Choose Winsok MOSFETs for Switching Applications?
- Industry-leading RDS(on) specifications
- Advanced packaging solutions
- Comprehensive application support
- Extensive product portfolio
- Proven reliability and performance
| Product Series | Key Features | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| WS-Power Series | Ultra-low RDS(on), high current capability | Power conversion, motor drives |
| WS-Logic Series | Logic-level gate drive, fast switching | Digital systems, signal switching |
| WS-Auto Series | AEC-Q100 qualified, robust design | Automotive applications |
Technical Support and Resources
At Winsok MOSFETs, we provide comprehensive technical support to ensure your switching applications achieve optimal performance:
- SPICE models for circuit simulation
- Detailed application notes
- Technical documentation
- Design review services
- Thermal analysis support
Contact Our Switching Applications Experts
Ready to optimize your switching application with Winsok MOSFETs? Our technical team is here to help you select the perfect MOSFET and design your switching circuit for maximum efficiency and reliability.