Looking to master MOSFET amplifiers? You’re in the right place. This comprehensive guide breaks down everything from fundamental concepts to cutting-edge applications, helping you understand the various types of MOSFET amplifiers and their practical implementations.
Understanding MOSFET Amplifier Fundamentals
MOSFET amplifiers have revolutionized modern electronics, offering superior performance in terms of power efficiency, frequency response, and circuit simplicity. Before diving into specific types, let’s understand what makes MOSFET amplifiers special.
Key Advantages of MOSFET Amplifiers
- Higher input impedance compared to BJT amplifiers
- Better thermal stability
- Lower noise characteristics
- Excellent switching characteristics
- Minimal distortion at high frequencies
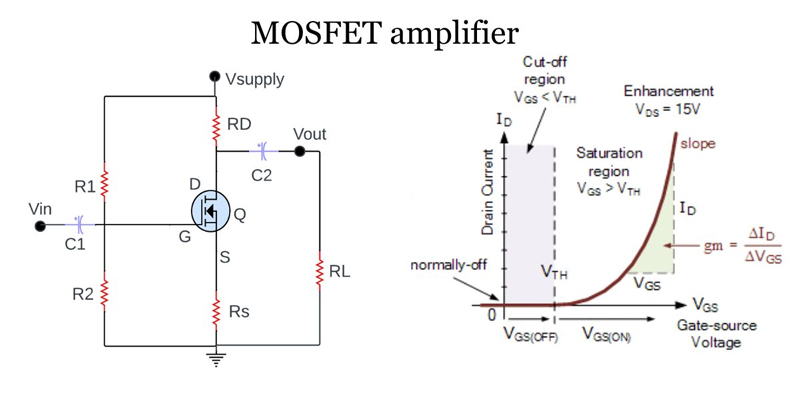
Common Source Amplifier: The Fundamental Building Block
The common source (CS) amplifier is the MOSFET equivalent of the common emitter BJT configuration. It’s the most widely used MOSFET amplifier type due to its versatility and performance characteristics.
| Parameter | Characteristic | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Gain | High (180° phase shift) | General purpose amplification |
| Input Impedance | Very High | Voltage amplification stages |
| Output Impedance | Moderate to High | Voltage amplification stages |
Common Drain (Source Follower) Amplifier
The common drain configuration, also known as the source follower, is ideal for impedance matching and buffering applications.
Key Features:
- Unity voltage gain
- No phase inversion
- Very high input impedance
- Low output impedance
Common Gate Amplifier Configuration
While less common than CS or CD configurations, the common gate amplifier offers unique advantages in specific applications:
| Characteristic | Value | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Input Impedance | Low | Good for current-source inputs |
| Output Impedance | High | Excellent isolation |
| Frequency Response | Excellent | Suitable for high-frequency applications |
Cascode Amplifier: Advanced Configuration
The cascode amplifier combines the best features of common source and common gate configurations, offering:
- Improved frequency response
- Better isolation
- Reduced Miller effect
- Higher output impedance
Power MOSFET Amplifiers
Applications in Audio Systems:
- Class AB audio amplifiers
- Class D switching amplifiers
- High-power sound systems
- Car audio amplifiers
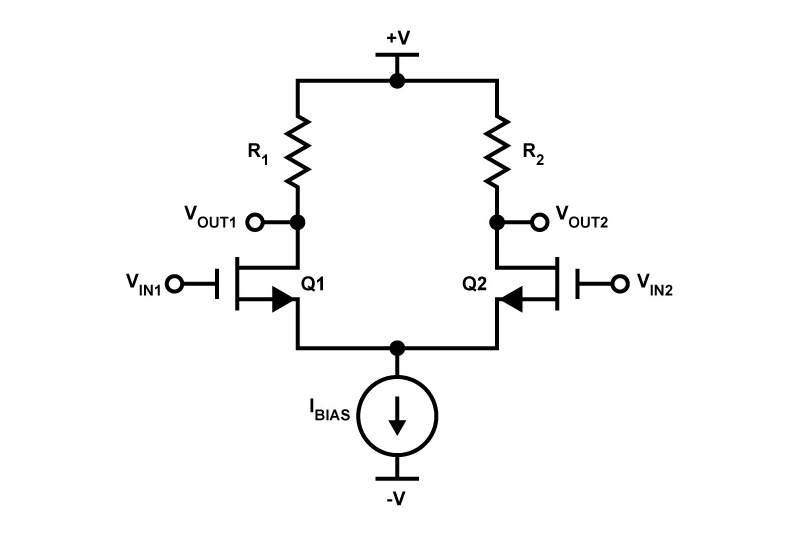
Differential MOSFET Amplifiers
Differential amplifiers using MOSFETs are crucial in:
- Operational amplifiers
- Instrumentation amplifiers
- Analog-to-digital converters
- Sensor interfaces
Practical Design Considerations
| Design Aspect | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Biasing | Proper DC operating point selection |
| Thermal Management | Heat dissipation and stability |
| Frequency Compensation | Stability at high frequencies |
| Layout Considerations | Minimizing parasitic effects |
Need Professional MOSFET Amplifier Solutions?
Our expert team specializes in custom MOSFET amplifier designs for any application. Get access to:
- Custom design services
- Technical consultation
- Component selection
- Performance optimization
Advanced Topics and Future Trends
Stay ahead of the curve with emerging trends in MOSFET amplifier technology:
- GaN MOSFET applications
- Silicon carbide devices
- Advanced packaging technologies
- Integration with digital systems
Get Our Complete MOSFET Amplifier Design Guide
Get instant access to our comprehensive design guide, including schematics, calculations, and best practices.