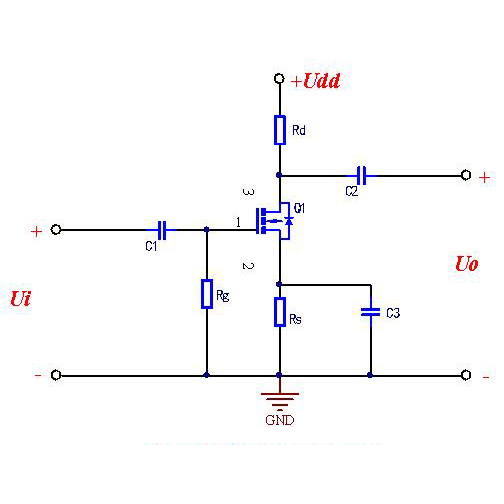
The inverter's MOSFET operates in a switching state and the current flowing through the MOSFET is very high. If the MOSFET is not properly selected, the driving voltage amplitude is not large enough or the circuit heat dissipation is not good, it may cause the MOSFET to heat up.
1, inverter MOSFET heating is serious, should pay attention to the MOSFET selection
MOSFET in the inverter in the switching state, generally require its drain current as large as possible, on-resistance as small as possible, so that you can reduce the saturation voltage drop of the MOSFET, thereby reducing the MOSFET since the consumption, reduce the heat.
Check the MOSFET manual, we will find that the higher the withstand voltage value of the MOSFET, the greater its on-resistance, and those with high drain current, low withstand voltage value of the MOSFET, its on-resistance is generally below tens of milliohms.
Assuming that the load current of 5A, we choose the inverter commonly used MOSFETRU75N08R and withstand voltage value of 500V 840 can be, their drain current are in 5A or more, but the on-resistance of the two MOSFETs are different, drive the same current, their heat difference is very large. 75N08R on-resistance is only 0.008Ω, while the on-resistance of 840 The on-resistance of 75N08R is only 0.008Ω, while the on-resistance of 840 is 0.85Ω. When the load current flowing through the MOSFET is 5A, the voltage drop of 75N08R's MOSFET is only 0.04V, and the MOSFET consumption of MOSFET is only 0.2W, while the voltage drop of 840's MOSFET can be up to 4.25W, and the consumption of MOSFET is as high as 21.25W. From this, it can be seen that the on-resistance of MOSFET is different from the on-resistance of 75N08R, and their heat generation is very much different. The smaller the on-resistance of the MOSFET, the better, the on-resistance of the MOSFET, the MOSFET tube under high current consumption is quite large.
2, the driving circuit of the driving voltage amplitude is not large enough
MOSFET is a voltage control device, if you want to reduce the MOSFET tube consumption, reduce heat, MOSFET gate drive voltage amplitude should be large enough, drive pulse edge to steep, can reduce the MOSFET tube voltage drop, reduce MOSFET tube consumption.
3, MOSFET heat dissipation is not good cause
Inverter MOSFET heating is serious. As the inverter MOSFET tube consumption is large, the work generally requires a large enough external area of the heat sink, and the external heat sink and the MOSFET itself between the heat sink should be in close contact (generally required to be coated with thermally conductive silicone grease), if the external heat sink is smaller, or with the MOSFET itself is not close enough to the contact of the heat sink, may lead to MOSFET heating.
Inverter MOSFET heating serious there are four reasons for the summary.
MOSFET slight heating is a normal phenomenon, but the heating is serious, and even lead to the MOSFET is burned, there are the following four reasons:
1, the problem of circuit design
Let the MOSFET work in a linear operating state, rather than in the switching circuit state. It is also one of the causes of MOSFET heating. If the N-MOS is doing the switching, the G-level voltage has to be a few V higher than the power supply to be fully on, while the P-MOS is the opposite. Not fully open and the voltage drop is too large resulting in power consumption, the equivalent DC impedance is larger, the voltage drop increases, so U * I also increases, the loss means heat. This is the most avoided error in the design of the circuit.
2, too high a frequency
The main reason is that sometimes the excessive pursuit of volume, resulting in increased frequency, MOSFET losses on the large, so the heat is also increased.
3, not enough thermal design
If the current is too high, the nominal current value of the MOSFET, usually requires good heat dissipation to achieve. So the ID is less than the maximum current, it may also heat up badly, need enough auxiliary heat sink.
4, MOSFET selection is wrong
Wrong judgment of power, MOSFET internal resistance is not fully considered, resulting in increased switching impedance.