1. Voltage-Controlled Operation
Unlike bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) which are current-controlled devices, power MOSFETs are voltage-controlled. This fundamental characteristic offers several significant benefits:
- Simplified gate drive requirements
- Lower power consumption in the control circuit
- Faster switching capabilities
- No secondary breakdown concerns
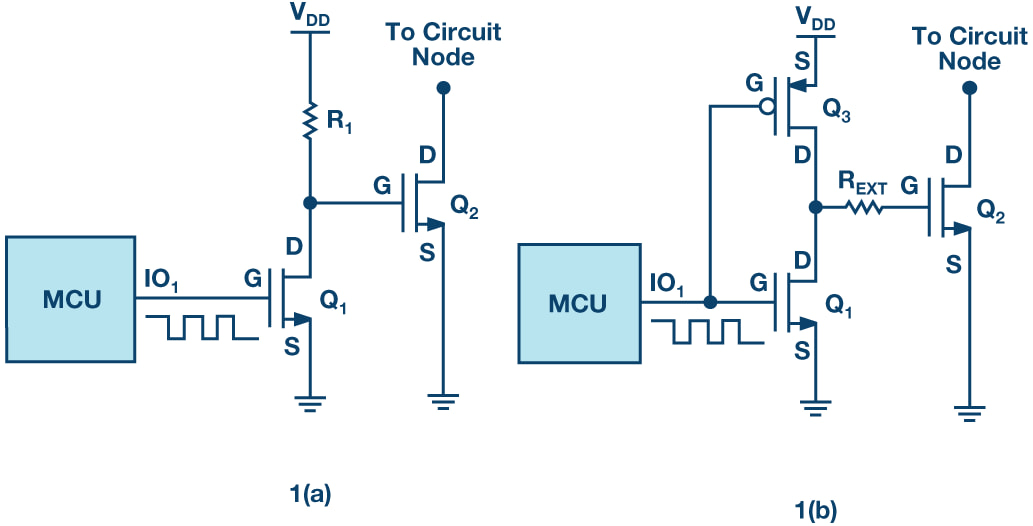
Figure 1: Simplified gate drive requirements of MOSFETs compared to BJTs
2. Superior Switching Performance
Power MOSFETs excel in high-frequency switching applications, offering numerous advantages over traditional BJTs:
Figure 2: Switching speed comparison between MOSFET and BJT
| Parameter | Power MOSFET | BJT |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Speed | Very Fast (ns range) | Moderate (μs range) |
| Switching Losses | Low | High |
| Maximum Switching Frequency | >1 MHz | ~100 kHz |
3. Thermal Characteristics
Power MOSFETs exhibit superior thermal characteristics that contribute to their reliability and performance:
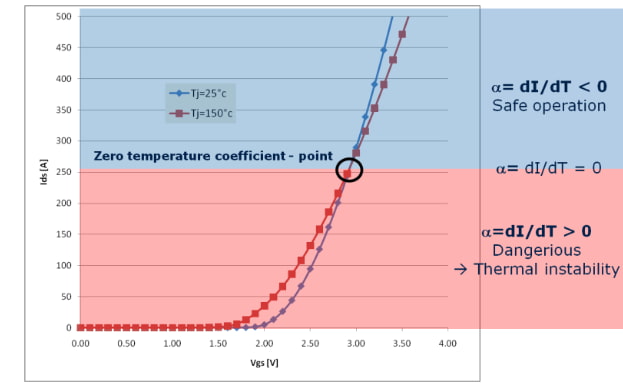
Figure 3: Temperature coefficient of RDS(on) in power MOSFETs
- Positive temperature coefficient prevents thermal runaway
- Better current sharing in parallel operation
- Higher thermal stability
- Wider safe operating area (SOA)
4. Low On-State Resistance
Modern power MOSFETs achieve extremely low on-state resistance (RDS(on)), leading to several benefits:
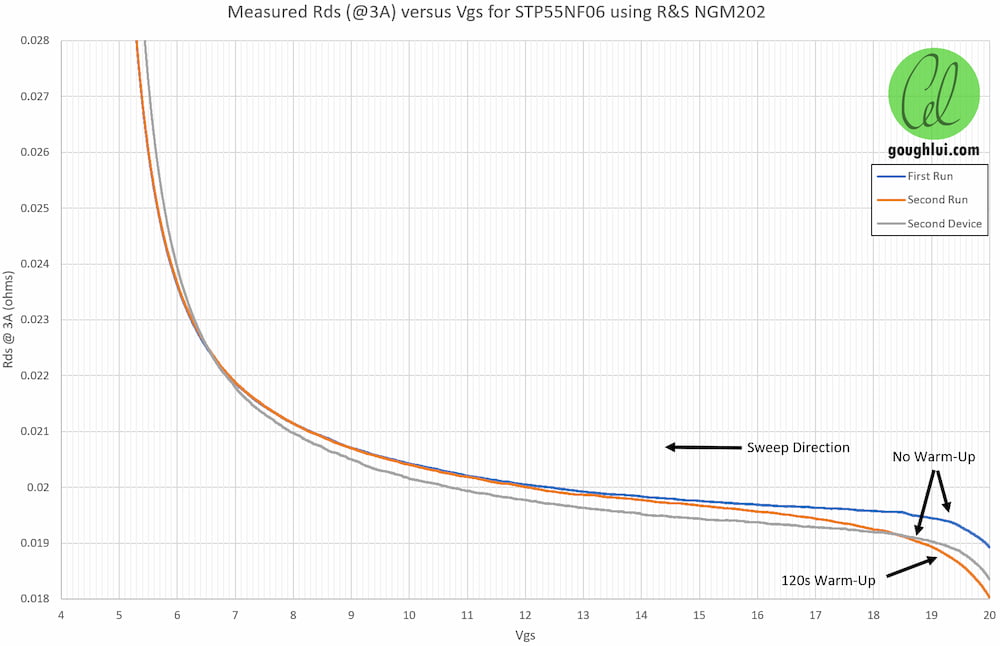
Figure 4: Historical improvement in MOSFET RDS(on)
5. Paralleling Capability
Power MOSFETs can be easily connected in parallel to handle higher currents, thanks to their positive temperature coefficient:
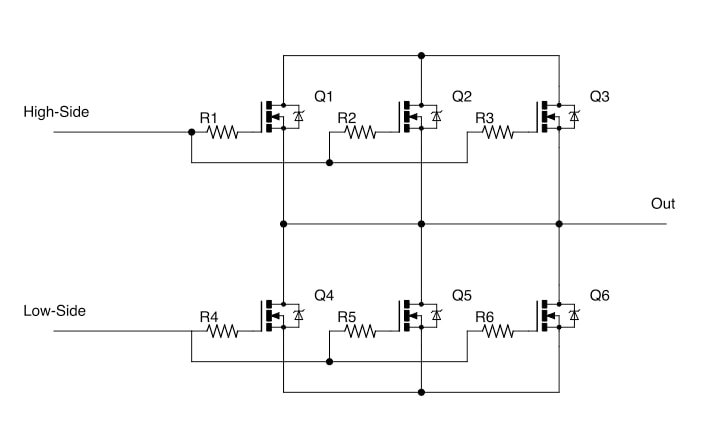
Figure 5: Current sharing in parallel-connected MOSFETs
6. Ruggedness and Reliability
Power MOSFETs offer excellent ruggedness and reliability features:
- No secondary breakdown phenomenon
- Inherent body diode for reverse voltage protection
- Excellent avalanche capability
- High dV/dt capability
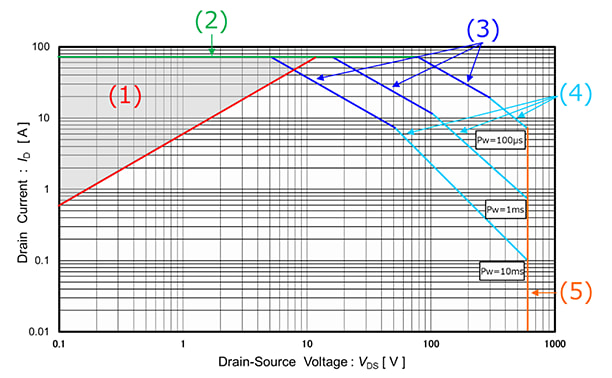
Figure 6: Safe Operating Area (SOA) comparison between MOSFET and BJT
7. Cost-Effectiveness
While individual power MOSFETs might have a higher initial cost compared to BJTs, their overall system-level benefits often result in cost savings:
- Simplified drive circuits reduce component count
- Higher efficiency reduces cooling requirements
- Higher reliability reduces maintenance costs
- Smaller size enables compact designs
8. Future Trends and Improvements
The advantages of power MOSFETs continue to improve with technological advancements:
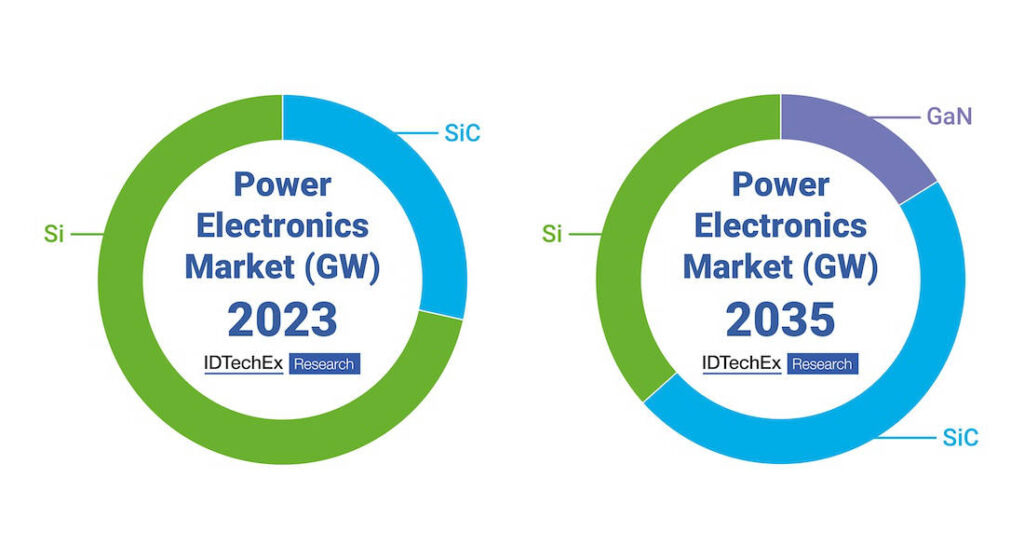
Figure 7: Evolution and future trends in power MOSFET technology













