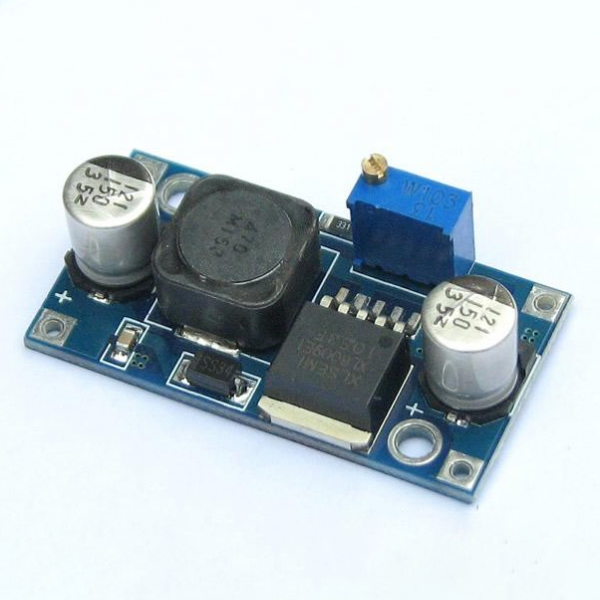
As one of the most basic devices in the semiconductor field, MOSFETs are widely used in both IC design and board-level circuits. At present, especially in the field of high-power semiconductors, a variety of different structures of MOSFETs also play an irreplaceable role. For MOSFETs, the structure of which can be said to be a set of simple and complex in one, simple is simple in its structure, complex is based on the application of its in-depth consideration. In the day-to-day, MOSFET heat is also considered a very common situation, the key we need to know the reasons from where, and what methods can be solved? Next let us come together to understand.
I. Causes of MOSFET heating
1, the problem of circuit design. It is to let the MOSFET work in the online state, not in the switching state. This is one of the reasons why the MOSFET gets hot. If the N-MOS does the switching, the G-level voltage has to be a few V higher than the power supply in order to be fully on, and the opposite is true for the P-MOS. Not fully open and the voltage drop is too large resulting in power consumption, the equivalent DC impedance is relatively large, the voltage drop increases, so U * I also increases, the loss means heat.
2, the frequency is too high. Mainly sometimes too much for the volume, resulting in increased frequency, MOSFET losses on the increase, which also leads to MOSFET heating.
3, the current is too high. When the ID is less than the maximum current, it will also cause the MOSFET to heat up.
4, the choice of the MOSFET model is wrong. The internal resistance of the MOSFET is not fully considered, resulting in increased switching impedance.二、
The solution for MOSFET's severe heat generation
1, Do a good job on the heat sink design of the MOSFET.
2, Add enough auxiliary heat sinks.
3, Paste the heat sink adhesive.