Why MOSFETs Matter in Modern Electronics
Ever wondered how your smartphone can pack so much computing power into such a tiny space? The answer lies in one of the most revolutionary inventions in electronics: the MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor). Whether you’re a hobbyist, student, or just curious about electronics, understanding MOSFETs is crucial in today’s digital age.
What Exactly is a MOSFET?
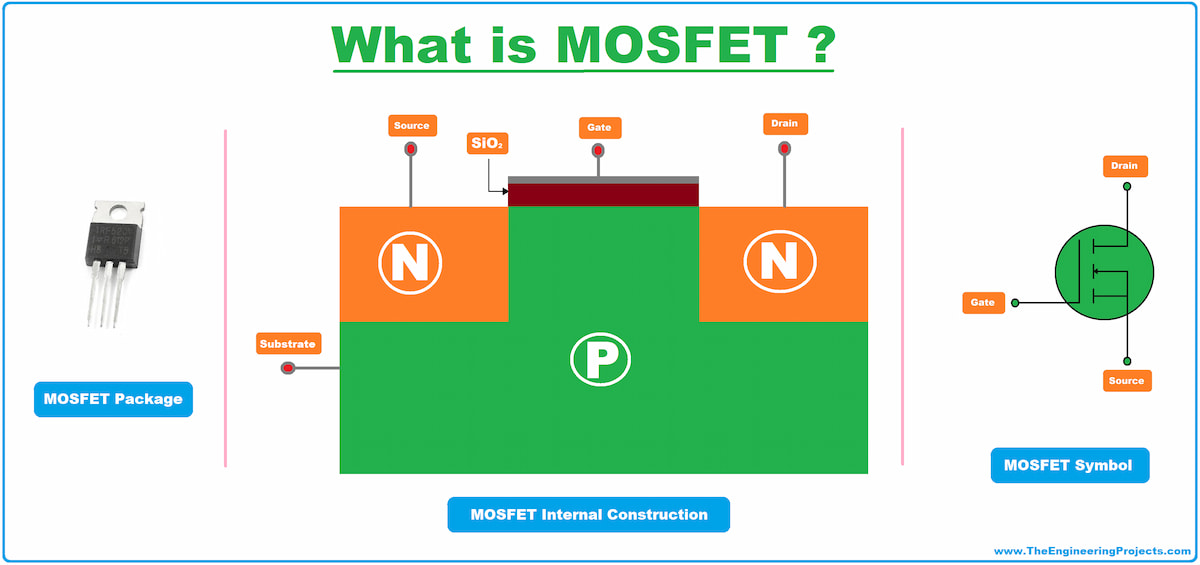
Think of a MOSFET as a tiny electronic switch that can control the flow of electricity. Unlike traditional mechanical switches, MOSFETs have no moving parts and can switch thousands or even millions of times per second. They’re the fundamental building blocks of modern digital electronics, from simple LED controllers to complex microprocessors.
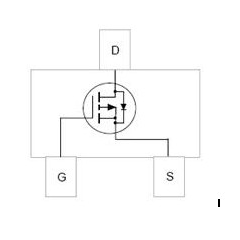
Basic Structure of a MOSFET
| Terminal | Function | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Gate (G) | Controls current flow | Like a water tap handle |
| Source (S) | Where current enters | Like a water source |
| Drain (D) | Where current exits | Like a water drain |
Types of MOSFETs: N-Channel vs P-Channel
MOSFETs come in two main flavors: N-channel and P-channel. Think of them as complementary tools in your electronic toolbox. N-channel MOSFETs are like right-handed tools (more common and typically cheaper), while P-channel MOSFETs are like left-handed tools (less common but essential for specific applications).
Key Differences
- N-channel: Turns ON with positive gate voltage
- P-channel: Turns ON with negative gate voltage
- N-channel: Generally lower RDS(on) resistance
- P-channel: Simpler circuit design in some cases
Common Applications of MOSFETs
MOSFETs are incredibly versatile components. Here are some common applications:
- Power supplies and voltage regulators
- Motor controllers and PWM circuits
- LED drivers and lighting control
- Audio amplifiers
- Battery-powered devices
Choosing the Right MOSFET
Selecting the appropriate MOSFET for your application involves considering several key parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| VDS(max) | Maximum drain-source voltage | 20V – 800V |
| ID(max) | Maximum drain current | 1A – 100A |
| RDS(on) | On-state resistance | 1mΩ – 100mΩ |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with MOSFETs, beginners often make these mistakes:
- Forgetting about gate protection
- Ignoring thermal management
- Incorrect gate drive voltage
- Poor PCB layout practices
Advanced Topics
Gate Drive Considerations
Proper gate driving is crucial for optimal MOSFET performance. Consider these factors:
- Gate threshold voltage (VGS(th))
- Gate charge (Qg)
- Switching speed requirements
- Drive circuit topology
Thermal Management
Power MOSFETs can generate significant heat during operation. Effective thermal management involves:
- Proper heatsink selection
- Thermal interface materials
- Air flow considerations
- Temperature monitoring
Need Professional MOSFET Solutions?
At Olukey, we offer a wide range of high-quality MOSFETs for all applications. Our team of experts can help you select the perfect MOSFET for your specific needs.
Additional Resources
Want to learn more about MOSFETs? Check out these valuable resources:
- Detailed application notes
- Design guidelines
- Technical specifications
- Sample circuits