Expert Overview: Discover how Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) technology revolutionizes electronic switching applications with unparalleled efficiency and reliability.
Fundamentals of CMOS Switch Operation
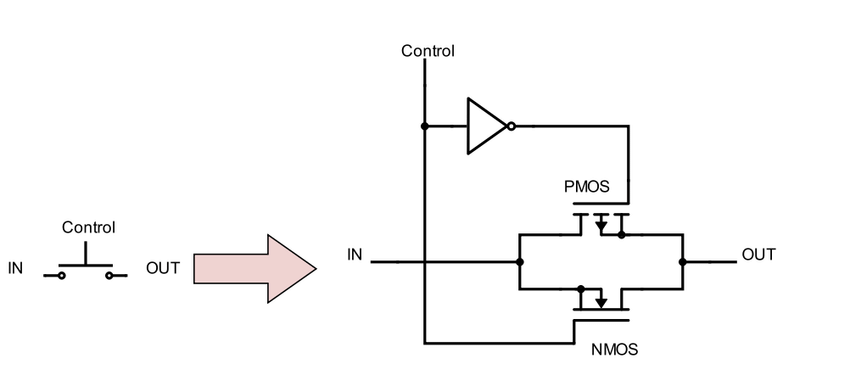 CMOS technology combines both NMOS and PMOS transistors to create highly efficient switching circuits with near-zero static power consumption. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate workings of CMOS switches and their applications in modern electronics.
CMOS technology combines both NMOS and PMOS transistors to create highly efficient switching circuits with near-zero static power consumption. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate workings of CMOS switches and their applications in modern electronics.
Basic CMOS Structure
- Complementary pair configuration (NMOS + PMOS)
- Push-pull output stage
- Symmetrical switching characteristics
- Built-in noise immunity
CMOS Switch Operating Principles
Switching States Analysis
| State | PMOS | NMOS | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logic High Input | OFF | ON | LOW |
| Logic Low Input | ON | OFF | HIGH |
| Transition | Switching | Switching | Changing |
Key Advantages of CMOS Switches
- Extremely low static power consumption
- High noise immunity
- Wide operating voltage range
- High input impedance
CMOS Switch Applications
Digital Logic Implementation
- Logic gates and buffers
- Flip-flops and latches
- Memory cells
- Digital signal processing
Analog Switch Applications
- Signal Multiplexing
- Audio routing
- Video switching
- Sensor input selection
- Sample and Hold Circuits
- Data acquisition
- ADC front-end
- Signal processing
Design Considerations for CMOS Switches
Critical Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| RON | On-state resistance | Signal integrity, power loss |
| Charge injection | Switching transients | Signal distortion |
| Bandwidth | Frequency response | Signal handling capability |
Professional Design Support
Our expert team provides comprehensive design support for your CMOS switch applications. From component selection to system optimization, we ensure your success.
Protection and Reliability
- ESD protection strategies
- Latch-up prevention
- Power supply sequencing
- Temperature considerations
Advanced CMOS Technologies
Latest Innovations
- Sub-micron process technologies
- Low voltage operation
- Enhanced ESD protection
- Improved switching speeds
Industry Applications
- Consumer electronics
- Industrial automation
- Medical devices
- Automotive systems
Partner With Us
Choose our cutting-edge CMOS solutions for your next project. We offer competitive pricing, reliable delivery, and outstanding technical support.
CMOS Timing and Propagation Delay
Understanding timing characteristics is crucial for optimal CMOS switch implementation. Let’s explore the key timing parameters and their impact on system performance.
Critical Timing Parameters
| Parameter | Definition | Typical Range | Affecting Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rise Time | Time for output to rise from 10% to 90% | 1-10ns | Load capacitance, supply voltage |
| Fall Time | Time for output to fall from 90% to 10% | 1-10ns | Load capacitance, transistor sizing |
| Propagation Delay | Input to output delay | 2-20ns | Process technology, temperature |
Power Consumption Analysis
Components of Power Dissipation
- Static Power Consumption
- Leakage current effects
- Subthreshold conduction
- Temperature dependence
- Dynamic Power Consumption
- Switching power
- Short-circuit power
- Frequency dependence
Layout and Implementation Guidelines
Best Practices for PCB Design
- Signal integrity considerations
- Trace length matching
- Impedance control
- Ground plane design
- Power distribution optimization
- Decoupling capacitor placement
- Power plane design
- Star grounding techniques
- Thermal management strategies
- Component spacing
- Thermal relief patterns
- Cooling considerations
Testing and Verification Methods
Recommended Test Procedures
| Test Type | Parameters Tested | Equipment Required |
|---|---|---|
| DC Characterization | VOH, VOL, VIH, VIL | Digital multimeter, power supply |
| AC Performance | Switching speed, propagation delay | Oscilloscope, function generator |
| Load Testing | Drive capability, stability | Electronic load, thermal camera |
Quality Assurance Program
Our comprehensive testing program ensures every CMOS device meets stringent quality standards:
- 100% functional testing at multiple temperatures
- Statistical process control
- Reliability stress testing
- Long-term stability verification
Environmental Considerations
Operating Conditions and Reliability
- Temperature range specifications
- Commercial: 0°C to 70°C
- Industrial: -40°C to 85°C
- Automotive: -40°C to 125°C
- Humidity effects
- Moisture sensitivity levels
- Protection strategies
- Storage requirements
- Environmental compliance
- RoHS compliance
- REACH regulations
- Green initiatives
Cost Optimization Strategies
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
- Initial component costs
- Implementation expenses
- Operating costs
- Power consumption
- Cooling requirements
- Maintenance needs
- Lifetime value considerations
- Reliability factors
- Replacement costs
- Upgrade paths
Technical Support Package
Take advantage of our comprehensive support services:
- Design consultation and review
- Application-specific optimization
- Thermal analysis assistance
- Reliability prediction models