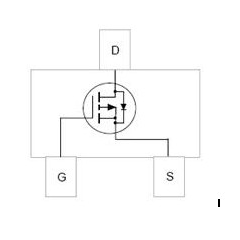
MOSFET, known as Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor, is a widely used electronic device that belongs to a type of Field-Effect Transistor (FET).The main structure of a MOSFET consists of a metal gate, an oxide insulating layer (usually Silicon Dioxide SiO₂) and a semiconductor layer (usually silicon Si). The principle of operation is to control the gate voltage to change the electric field on the surface or inside the semiconductor, thus controlling the current between the source and drain.
MOSFETs can be categorized into two main types: N-channel MOSFETs (NMOS) and P-channel MOSFETs (PMOS). In NMOS, when the gate voltage is positive with respect to the source, n-type conducting channels are formed on the semiconductor surface, allowing electrons to flow from the source to the drain. In PMOS, when the gate voltage is negative with respect to the source, p-type conducting channels are formed on the semiconductor surface, allowing holes to flow from the source to the drain.
MOSFETs have many advantages, such as high input impedance, low noise, low power consumption, and ease of integration, so they are widely used in analog circuits, digital circuits, power management, power electronics, communication systems, and other fields. In integrated circuits, MOSFETs are the basic units that make up CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) logic circuits. CMOS circuits combine the advantages of NMOS and PMOS, and are characterized by low power consumption, high speed and high integration.
In addition, MOSFETs can be categorized into enhancement-type and depletion-type according to whether their conducting channels are pre-formed. Enhancement type MOSFET in the gate voltage is zero when the channel is not conductive, need to apply a certain gate voltage to form a conductive channel; while depletion type MOSFET in the gate voltage is zero when the channel is already conductive, the gate voltage is used to control the conductivity of the channel.
In summary, MOSFET is a field effect transistor based on a metal oxide semiconductor structure, which regulates the current between source and drain by controlling the gate voltage, and has a wide range of applications and important technical value.