I. Definition of MOSFET
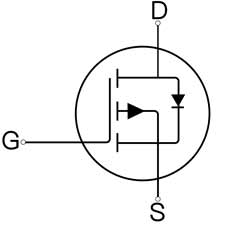
As a voltage-driven, high-current devices, MOSFETs have a large number of applications in circuits, especially power systems. MOSFET body diodes, also known as parasitic diodes, are not found in the lithography of integrated circuits, but are found in separate MOSFET devices, which provide reverse protection and current continuation when driven by high currents and when inductive loads are present.
Due to the presence of this diode, the MOSFET device cannot simply be seen switching in a circuit, as in a charging circuit where charging is finished, power is removed and the battery reverses outward, which is usually an unwanted result.
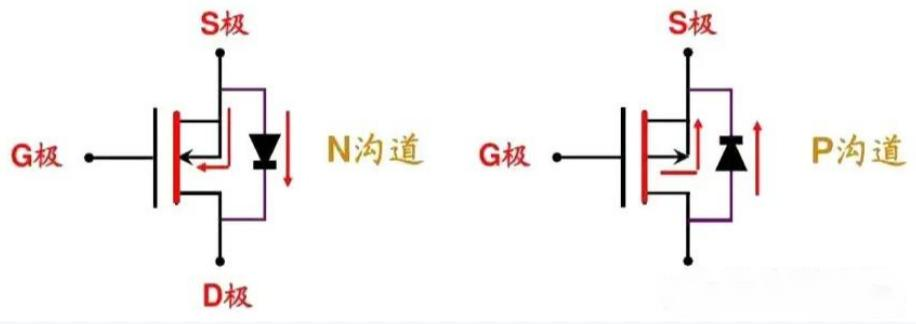
The general solution is to add a diode at the back to prevent reverse power supply, but the characteristics of the diode determine the need for a forward voltage drop of 0.6~1V, which results in a serious heat generation at high currents while causing a waste of energy and reducing the overall energy efficiency. Another method is to append a back-to-back MOSFET, utilizing the low on-resistance of the MOSFET to achieve energy efficiency.
It should be noted that after conduction, the MOSFET's non-directional, so after pressurized conduction, it is equivalent to with a wire, only resistive, no on-state voltage drop, usually saturated on-resistance for a few milliohms to timely milliohms, and non-directional, allowing DC and AC power to pass.
II. Characteristics of MOSFETs
1, MOSFET is a voltage-controlled device, no propulsion stage is needed to drive high currents;
2、High input resistance;
3, wide operating frequency range, high switching speed, low loss
4, AC comfortable high impedance, low noise.
5、Multiple parallel use, increase output current
Second, the use of MOSFETs in the process of precautions
1, in order to ensure the safe use of MOSFET, in the line design, should not exceed the pipeline power dissipation, maximum leakage source voltage, gate source voltage and current and other parameter limit values.
2, various types of MOSFETs in use, must be strictly in accordance with the required bias access to the circuit, to comply with the polarity of the MOSFET offset.
3. When installing the MOSFET, pay attention to the installation position to avoid close to the heating element. In order to prevent vibration of the fittings, the shell must be tightened; bending the pin leads should be carried out at greater than the root size of 5mm to prevent the pin from bending off and leakage.
4, due to the extremely high input impedance, MOSFETs must be shorted out of the pin during transportation and storage, and packaged with metal shielding to prevent external induced potential breakdown of the gate.
5. The gate voltage of junction MOSFETs cannot be reversed and can be stored in an open-circuit state, but the input resistance of insulated-gate MOSFETs is very high when they are not in use, so each electrode must be short-circuited. When soldering insulated-gate MOSFETs, follow the order of source-drain-gate, and solder with power off.
To ensure the safe use of MOSFETs, you need to understand fully understand the characteristics of MOSFETs and the precautions to be taken in the use of the process, I hope that the above summary will help you.