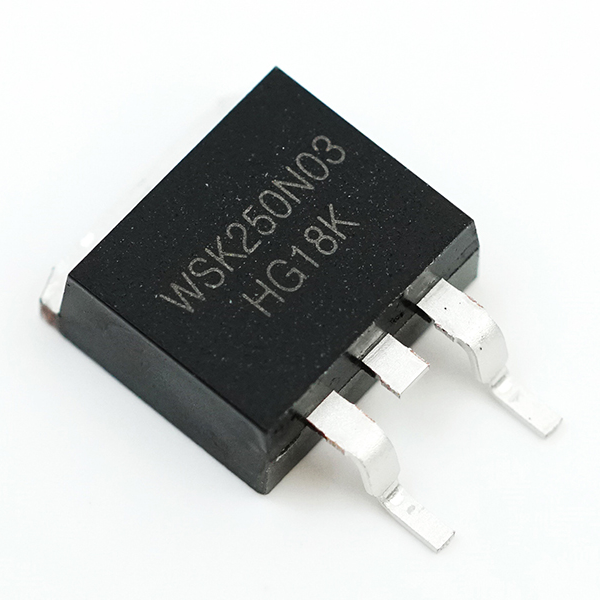
1.Junction MOSFET pin identification
The gate of the MOSFET is the base of the transistor, and the drain and source are the collector and emitter of the corresponding transistor. The multimeter to R × 1k gear, with two pens to measure the forward and reverse resistance between the two pins. When a two-pin forward resistance = reverse resistance = KΩ, that is, the two pins for the source S and drain D, the rest of the pin is the gate G. If it is a 4-pin junction MOSFET, the other pole is the use of grounded shield.
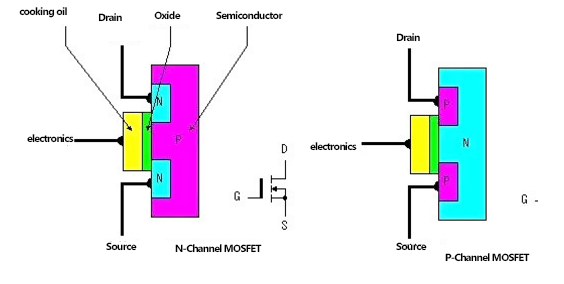
2.Determine the gate
With the black pen of the multimeter to touch the MOSFET a random electrode, the red pen to touch the other two electrodes. If both measured resistance is small, indicating that both are positive resistance, the tube belongs to the N-channel MOSFET, the same black pen contact is also the gate.
The production process has decided that the drain and source of the MOSFET is symmetrical, and can be exchanged with each other, and will not affect the use of the circuit, the circuit is also normal at this time, so there is no need to go to excessive distinction. The resistance between the drain and source is about a few thousand ohms. Can not use this method to determine the gate of the insulated gate type MOSFET. Because the resistance of the input of this MOSFET is extremely high, and the inter-polar capacitance between the gate and source is very small, the measurement of as little as a small amount of charge, can be formed on top of the inter-polar capacitance of the extremely high voltage, the MOSFET will be very easy to damage.
3.Estimating the amplification capability of MOSFETs
When the multimeter is set to R × 100, use the red pen to connect the source S, and use the black pen to connect the drain D, which is like adding a 1.5V voltage to the MOSFET. At this time the needle indicates the resistance value between the D-S pole. At this time with a finger to pinch the gate G, the body's induced voltage as an input signal to the gate. Because of the role of MOSFET amplification, ID and UDS will change, meaning that the resistance between the D-S pole has changed, we can observe that the needle has a large swing amplitude. If the hand pinch the gate, the swing of the needle is very small, that is, the MOSFET amplification ability is relatively weak; if the needle does not have the slightest action, indicating that the MOSFET has been damaged.