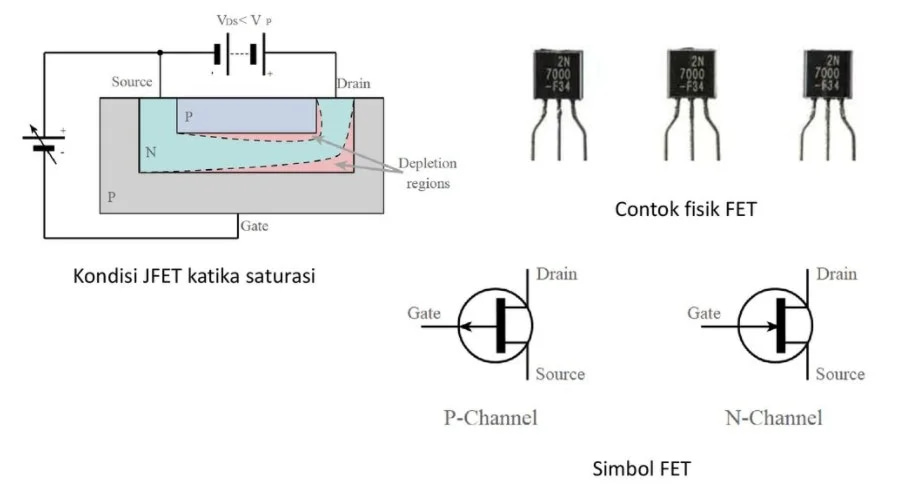
Understanding FET Basics
Before diving into circuit connections, it’s crucial to understand what FETs are and how they function. Field-Effect Transistors are voltage-controlled devices that regulate current flow in electronic circuits. Unlike bipolar junction transistors (BJTs), FETs operate by controlling an electrical field, making them more energy-efficient and easier to implement in many applications.
Types of FETs
- MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor FETs): Most common in modern electronics, especially in digital circuits and power applications
- JFETs (Junction FETs): Simpler structure, used in analog circuits and audio applications
- DEPFETs (Depleted FETs): Specialized type used in particular applications
Basic FET Circuit Connections
Connecting FET components properly is crucial for optimal circuit performance. Let’s explore the fundamental connection methods and configurations.
MOSFET Terminal Identification
| Terminal | Symbol | Function | Connection Guidelines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gate (G) | G | Control terminal | Connect to voltage control signal or bias voltage |
| Drain (D) | D | Main current path | Connect to load or power supply |
| Source (S) | S | Reference terminal | Usually connected to ground or common reference |
Common Circuit Configurations
1. Common Source Configuration
VDD
|
R
|
D
Vin--G| FET
S
|
GND
This is the most common configuration, providing voltage amplification and phase inversion. The input signal is applied to the gate, and the output is taken from the drain.
2. Common Drain Configuration
VDD
|
D
Vin--G| FET
S
|
R
|
GND
Also known as the source follower, this configuration provides current amplification with no voltage gain.
Advanced Connection Techniques
 When designing circuits with FETs from Winsok (available through Olukey), consider these advanced connection techniques for optimal performance:
When designing circuits with FETs from Winsok (available through Olukey), consider these advanced connection techniques for optimal performance:
- Gate protection circuits for static discharge prevention
- Heat sinking considerations for power applications
- Proper bypassing and decoupling techniques
Gate Protection Circuits
Protect your valuable Winsok FETs with these essential gate protection methods:
- Include a gate-source resistor (typically 10kΩ-100kΩ)
- Add protection diodes for high-voltage applications
- Use Zener diodes for voltage clamping
Troubleshooting Common Issues
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| FET Not Switching | Insufficient Gate Voltage | Check gate voltage levels and ensure proper drive |
| Overheating | Improper Heat Dissipation | Add or improve heat sink mounting |
| Oscillation | Poor Layout/Bypassing | Improve PCB layout and add proper bypass capacitors |
Best Practices for Circuit Design
PCB Layout Guidelines
- Keep gate traces short and away from high-current paths
- Use proper thermal relief for power devices
- Include adequate copper pour for heat dissipation
- Place bypass capacitors close to power pins
Applications and Case Studies
Winsok FETs, available through Olukey, are successfully used in various applications:
- Power supplies and voltage regulators
- Motor control circuits
- LED drivers and lighting controllers
- Audio amplifiers
- Battery management systems
Conclusion
Proper FET connection is crucial for circuit performance and reliability. By following these guidelines and using high-quality components from trusted manufacturers like Winsok, you can ensure optimal results in your electronic designs.