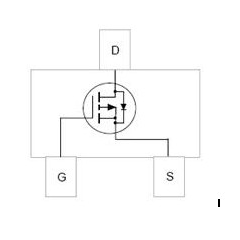
Field Effect Transistor abbreviated as MOSFET.There are two main types: junction field effect tubes and metal-oxide semiconductor field effect tubes. The MOSFET is also known as a unipolar transistor with a majority of carriers involved in the conductivity. They are voltage-controlled semiconductor devices. Due to its high input resistance, low noise, low power consumption, and other characteristics, making it a strong competitor to bipolar transistors and power transistors.
I. Main parameters of MOSFET
1, DC parameters
Saturation drain current can be defined as the drain current corresponding to when the voltage between gate and source is equal to zero and the voltage between drain and source is greater than the pinch-off voltage.
Pinch-off voltage UP: The UGS required to reduce the ID to a small current when the UDS is certain;
Turn-on voltage UT: UGS required to bring ID to a certain value when UDS is certain.
2、AC Parameters
Low-frequency transconductance gm : Describes the control effect of gate and source voltage on drain current.
Inter-pole capacitance: the capacitance between the three electrodes of the MOSFET, the smaller the value, the better the performance.
3、Limit parameters
Drain, source breakdown voltage: when the drain current rises sharply, it will produce avalanche breakdown when the UDS.
Gate breakdown voltage: junction field effect tube normal operation, gate and source between the PN junction in the reverse bias state, the current is too large to produce breakdown.
II. Characteristics of MOSFETs
MOSFET has an amplification function and can form an amplified circuit. Compared with a triode, it has the following characteristics.
(1) The MOSFET is a voltage controlled device, and the potential is controlled by UGS;
(2) The current at the input of the MOSFET is extremely small, so its input resistance is very high;
(3) Its temperature stability is good because it uses majority carriers for conductivity;
(4) The voltage amplification coefficient of its amplification circuit is smaller than that of a triode;
(5) It is more resistant to radiation.
Third, MOSFET and transistor comparison
(1) MOSFET source, gate, drain and triode source, base, set point pole corresponds to the role of similar.
(2) MOSFET is a voltage-controlled current device, the amplification coefficient is small, the amplification ability is poor; triode is a current-controlled voltage device, the amplification ability is strong.
(3) MOSFET gate basically does not take current; and triode work, the base will absorb a certain current. Therefore, the MOSFET gate input resistance is higher than the triode input resistance.
(4) The conductive process of MOSFET has the participation of polytron, and the triode has the participation of two kinds of carriers, polytron and oligotron, and its concentration of oligotron is greatly affected by the temperature, radiation and other factors, therefore, MOSFET has better temperature stability and radiation resistance than transistor. MOSFET should be selected when the environmental conditions change a lot.
(5) When MOSFET is connected to the source metal and the substrate, the source and drain can be exchanged and the characteristics do not change much, while when the collector and emitter of the transistor are exchanged, the characteristics are different and the β value is reduced.
(6) The noise figure of MOSFET is small.
(7) MOSFET and triode can be composed of a variety of amplifier circuits and switching circuits, but the former consumes less power, high thermal stability, wide range of supply voltage, so it is widely used in large-scale and ultra-large-scale integrated circuits.
(8) The on-resistance of the triode is large, and the on-resistance of the MOSFET is small, so MOSFETs are generally used as switches with higher efficiency.