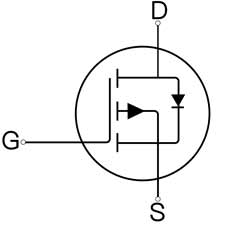
Depletion MOSFET, also known as MOSFET depletion, is an important operating state of field effect tubes. The following is a detailed description of it:
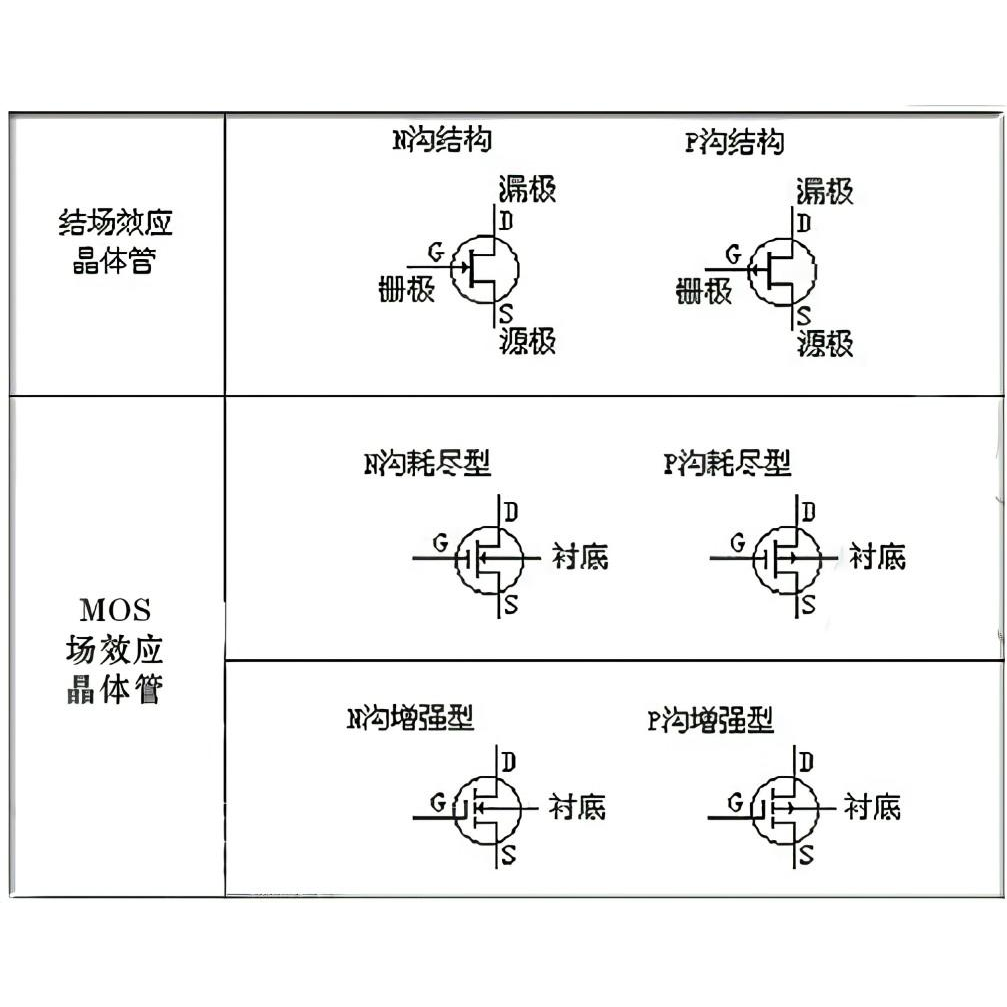
Definitions and Characteristics
DEFINITION: A depletion MOSFET is a special type of MOSFET that is able to conduct electricity because carriers are already present in its channel when the gate voltage is zero or within a specific range. This is in contrast to enhancement MOSFETs which require a certain value of gate voltage to form a conducting channel.
Characteristics: Depletion type MOSFET has the advantages of high input impedance, low leakage current and low switching impedance. These characteristics make it valuable for a wide range of applications in circuit design.
Working Principle
The operating principle of depletion MOSFETs can be controlled by changing the gate voltage to control the number of carriers in the channel and thus the current. The operating process can be summarized in the following stages:
Forbidden state: When the gate voltage is below the critical voltage between the channel and the source, the device is in the forbidden state and no current passes through the MOSFET.
Negative resistance state: As the gate voltage increases, charge begins to build up in the channel, creating a negative resistance effect. By adjusting the gate voltage, the strength of the negative resistance can be controlled, thus controlling the current in the channel.
ON STATE: When the gate voltage continues to increase beyond a critical voltage, the MOSFET enters the ON state and a large number of electrons and holes are transported through the channel, creating significant current.
Saturation: In the on state, the current in the channel reaches a saturation level, at which point continuing to increase the gate voltage no longer significantly increases the current.
Cutoff state (note: the description of "cutoff state" here may be slightly different from other literature because depletion MOSFETs always conduct under certain conditions): Under certain circumstances (e.g., an extreme change in gate voltage), a depletion MOSFET may enter a low-conducting state, but is not completely cutoff.
Application Areas
Depletion type MOSFETs have a wide range of applications in several fields due to their unique performance characteristics:
Power management: Utilizes its high input impedance and low leakage current characteristics to achieve efficient energy conversion in power management circuits.
Analog and digital circuits: play an important role in analog and digital circuits as switching elements or current sources.
Motor drive: precise control of motor speed and steering is realized by controlling the conduction and cut-off of MOSFETs.
Inverter Circuit: In solar power generation systems and radio communication systems, as one of the key components of the inverter, to realize the conversion of DC to AC.
Voltage regulator: By adjusting the size of the output voltage, it realizes the stable output of voltage and guarantees the normal work of electronic equipment.
caveat
In practical applications, it is necessary to select the appropriate depletion MOSFET model and parameters according to the specific needs.
Since depletion type MOSFETs operate differently from enhancement type MOSFETs, they require special attention in circuit design and optimization.
In summary, depletion type MOSFET, as an important electronic component, has a wide range of application prospects in the field of electronics. With the continuous progress of science and technology and the increase of application demand, its performance and application scope will also continue to expand and improve.